Category Archives: international affairs
Partnerships Matter: That City on the Hill; A Ship Adrift; A Lighthouse in the Tempest
India is the breakout partner for the US, defying what may once have seemed an improbable relationship.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s first state visit to the United States (US) came at a pivotal moment for global politics. It took place as communities across continents grappled with extreme economic volatility, polarised and sometimes violent public, and a breakdown of an unwritten yet impactful consensus on the benefits and utility of globalisation and global integration.
As Air India One touched down in New York for the first leg of Mr Modi’s visit, the Russian special military operation (invasion) in Ukraine was entering a new round of bloodletting. The European Union was just one incident away from further mayhem. The US was witnessing its most vicious conflict of recent time, the Battle of Pronouns. The liberal order, so assiduously crafted over the past seven decades by the transatlantic alliance, was neither liberal nor an order; it was simply adrift.
Once a proud people whose every whim became a global fad, it was now a country divided by identity, perverse politics, and an enduring uncertainty about the future beyond 2024.
Pax Americana was now just a nostalgic musing. The country that was identified by South Block’s brains trust as India’s most consequential partner in this century, was unrecognisable. Once a proud people whose every whim became a global fad, it was now a country divided by identity, perverse politics, and an enduring uncertainty about the future beyond 2024. Elections that are celebrations of pluralism elsewhere were now viewed with trepidation and anxiety.
In the last decades of the Roman Empire, life may not have been too different. A bloated sense of virtuosity and entitlement, obsession with gender and sexuality, and condescension towards those different to you were some among the common attributes. Add to that the always present dark underbelly of American society—racism. This was now all pervasive and normalised across the political spectrum, either as nationalist fervour or ‘woke’ swag.
And American media was taking it to the industrial scale through its partisan and uninformed reportage on its own people and on others. Orientalism was justifiable as freedom of expression was somehow a divine endowment that fed its preferred echo chambers. Cancel culture was popular culture. Newspapers once again became pamphlets, and gun culture was the manifestation of a society determined to shoot itself in the foot. The Supreme Court of the United States was indicted in its collaboration to disenfranchise half its population and become part of the political circus.
The Supreme Court of the United States was indicted in its collaboration to disenfranchise half its population and become part of the political circus.
Maybe it was time for another democracy and plural society to step in. It was the right moment for the US to hear PM Modi’s assertion that “India has proved that democracies can deliver […] regardless of class, creed, religion and gender” and “there is absolutely no space for discrimination”. This assertion has weight. It comes from a man leading a nation with more diverse communities, cultures, and customs than any other on the planet. The man who is committed to carry the largest democracy forward and cognisant of the challenge of defending pluralism in a world where disorder is the favoured operating system.
The state must serve the streets, not surrender to it was the Modi proposition.
For India, despite the recent developments, America was still the best bet. A superpower in decline was easier to negotiate with and seek bargains from. A people most like its own were easier to disagree with and yet, collaborate to build a basis for the broadly similar future we would share. Of course, as it did this it would need to develop a thick skin and rebuff the commentariat from the Beltway and challenge SoCal’s technology platforms that would promote hate, cancel speech, supress dissent, and amplify irrationality depending on the politics that mattered to them.
India’s cultural and constitutional realities would need to be protected even if it meant throwing the harsh end of the rule book at some technology behemoths and meddlesome institutions cloaking themselves under thew garb of virtuosity. The challenge for India was to do both even as it set about expanding the strategic content of its partnership with the Biden team. And it had to do this while seeking to preserve its geopolitical space in a world where choosing sides was an obsession.
India’s cultural and constitutional realities would need to be protected even if it meant throwing the harsh end of the rule book at some technology behemoths and meddlesome institutions cloaking themselves under thew garb of virtuosity.
Assertiveness and confidence defined PM Modi’s body language as he strode down the steps of Air India One. A day earlier, he had announced India’s position on Moscow: “We are not neutral. We are on the side of peace”—a message to both Russia and to the ‘neocons’, who had grabbed the media space and headlines recently. He also expressed confidence about bolstering India-US cooperation at forums like the G20, the Quad, and the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity. On American soil, he looked every inch the global leader who had put the idea of strategic alignment with the oldest democracy on steroids. This commitment was what he brought to the White House and raised the partnership five notches higher in tandem with President Biden who, despite domestic noise, turned up with his own resolutions.
First, India and the US have elevated their technology partnership to new heights. Both leaders hailed the launch of the Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies in January 2023, recommitting their countries to the creation of an open, accessible, and secure technology ecosystem. Defence cooperation received a major boost with a landmark agreement for the joint production of fighter jet engines in India. In the domain of civil space exploration, NASA and ISRO will undertake a joint mission to the International Space Station in 2024. And a Semiconductor Supply Chain and Innovation Partnership has been launched to galvanise both countries’ semiconductor programmes. In each case, India is the breakout partner for the US, defying what may once have seemed an improbable relationship.
Second, the wide-ranging defence deals—that also included the joint adoption of a Defence Industrial Cooperation Roadmap and the launch of the US-India Defence Acceleration Ecosystem—are not merely commercial transactions but indicative of a definite strategic direction. The co-production of jet engines; exercises in collaborative research, testing, and prototyping; and joint def-tech innovation all have implications beyond the deals themselves. They provide international stability and fortify India’s position as a strong, progressive nation. For the US, they act as investments in the Indo-Pacific construct and in a country that is now a geopolitically robust actor.
India is the breakout partner for the US, defying what may once have seemed an improbable relationship.
In a sense, the transfer of GE F414 jet engine technology and the sale of General Atomic predator drones in a government-to-government deal constitutes strengthening the frontline of democracy in the emerging geopolitical contest against authoritarianism. These platforms will be deployed where it counts; in contrast, constructs such as AUKUS are contingency planning.
Third, the rousing reception of PM Modi’s speech at the US Congress—and the 15 odd ovations he received for his celebration of the values of democracy, the unity of cultures, women’s empowerment, sustainable development, and technological advancement—more than drowned out the axis of drivel represented by the half-dozen members of Congress who chose to boycott his address. These were ad hominem voices that revel in false reason and pandering to perverse vote-banks. Their naysaying cannot undermine the stature of an Indian Prime Minister. The applause that reverberated through Congress was a vindication of Indian leadership, and of the PM’s belief that the “[India-US] relationship is prime for a momentous future, and that future is today”.
Fourth, the massive crowds of the Indian diaspora who gathered outside the White House to welcome PM Modi represented an evolution of the human bridge between the two countries. Even as they jostled for space and waved Indian and American flags, they stood for a community that sees both New Delhi and Washington, DC as its own and that will play a catalytic role in nurturing the partnership. Our domestic debates and contests will layer and colour the bilateral relationship, even as our domestic resolve will add steel to the partnership.
The applause that reverberated through Congress was a vindication of Indian leadership, and of the PM’s belief that the “[India-US] relationship is prime for a momentous future, and that future is today”.
The fifth and final “notch” has to do with continuity. The ties between the world’s oldest and largest democracies are enduring. From President Bush to Biden, with Obama and Trump in between, and from PM Vajpayee to Modi, with Manmohan Singh in between, we have seen heads of government on both sides staunchly committed to this relationship. Across parties, this has resulted in an abiding vision of a bipartisan future.
But it is now essential as well to recognise this partnership’s vitality for world affairs, its global impact on inclusive growth and development, and ultimately, on peace and prosperity. As the joint statement by the US and India puts it, “No corner of human enterprise is untouched by the partnership between [these] two great countries, which spans the seas to the stars.” It is time to invest in a global blueprint of this concert.
The present is muddy, the future is shared, and the possibilities are limitless.
India and the U.S. can together make tech more accessible to all
The growing partnership between India and the United States has the potential to shape both the global technology landscape and 21st-century geopolitics. The two democracies must ensure that technological advances work toward a more secure and prosperous world. There is already momentum: The U.S.-India initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET), announced last year, made strides to strengthen the connections between the U.S. and Indian innovation ecosystems in January. As Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi meets U.S. President Joe Biden in Washington this month, now is the moment to aim even higher.
Modi and Biden should convene a strategic technology partnership that cements high-level support for deepening cooperation in both the public and private sectors on innovation between India and the United States. That demands enhancing people-to-people connections, collaborating on expanding secure technology infrastructure around the world, developing standards of governance for new technologies, and engaging jointly with the global south on a democratic vision for the future.
Today, the shape of that future looks uncertain, and techno-authoritarians are on the march. It will take the collective strength of the democracies anchoring the Indo-Pacific region to chart a different course. To do so, they must unleash market forces that align with their strategic objectives. India and the United States need to sensitize investors, target large pools of available capital, and ensure that their ambitions never lack investments. India and the United States can together ensure tech opportunities are made broadly accessible.
Modi and Biden should convene a strategic technology partnership that cements high-level support for deepening cooperation in both the public and private sectors on innovation between India and the United States.
Amid growing technology competition, the United States remains a leader while India has leapt forward as an innovation powerhouse. Both countries have robust, educated workforces: The United States leads in producing Ph.Ds. in science and engineering, while India is ahead in terms of graduates with bachelor’s degrees in those subjects. India’s entrepreneurial environment is also blossoming. In 2021, the number of Indian unicorns—start-ups valued at more than $1 billion—increased from 40 to 108. The same year, Indian deep tech ventures—those that portend a large impact but require significant time and capital to reach markets—raised around $2.65 billion. In domains such as the commercial space sector, India is becoming a key global player. New Delhi is a capable partner for Washington in the entire innovation chain, from research and development to production.
Both countries recognize the opportunity presented by emerging technologies and seem willing to work together to seize it. In February, the Modi government announced that investments in new technologies, particularly in digital infrastructure, will underpin India’s path to become a developed nation by 2047. And in the United States, public and private sector interests are converging on a tech-focused approach to the future, starting with the CHIPS and Science Act. The countries have cooperated on smart city planning and defense technology transfers. On the latter, their defense technology partnership appears poised for significant elevation, given reports that the United States will allow General Electric to produce military jet engines—one of Washington’s most closely guarded secrets—in India.
A strategic partnership between India and the United States, focused on technology, will further the countries’ shared talent advantage. The two workforces are already interwoven, especially in the technology sector. In 2021, Indians accounted for 74 percent of all of U.S. H1-B visa allotments, and Indian employees have spurred innovation at many U.S. tech firms—to say nothing of the Indian Americans leading two of the largest companies in the world. A strategic partnership could focus on identifying opportunities and removing hurdles for people-to-people flows.
A first order of business for such a partnership could be to address the U.S. visa backlogs for Indian applicants, both workers and visitors. Creating programs to strengthen investor and entrepreneurial relationships between India and the United States should be another priority; doing so would deepen connections between private enterprises. The education technology sector offers promising opportunities in this regard. As U.S. edtech firms seek to gain a greater share of the Indian online learning market, India’s edtech firms are increasingly going global and entrenching themselves in the U.S. market and elsewhere. India and the United States should tap into this environment of constructive competition and collaboration.
As U.S. edtech firms seek to gain a greater share of the Indian online learning market, India’s edtech firms are increasingly going global and entrenching themselves in the U.S. market and elsewhere.
Next, a strategic technology partnership would invest in expanding the global infrastructure to support the digital world, particularly in the global south. Collaboration in this sphere could run the gamut: joint research and testing on beneficial disruptive technologies, manufacturing hardware, and even pooling funds for large-scale investments. India and the United States must also work together with their partners to highlight that in a world of increasing geopolitical, health, and climate risks, resilient supply chains will be an essential element of cooperation going forward. This year, India’s G-20 presidency offers a platform to further this discussion; green development, inclusive growth, and technological transformation are at the heart of New Delhi’s G-20 agenda.
India and the United States each bring a necessary piece of digital infrastructure to the table. For its part, India is a leader in testing Open-Radio Access Networks (O-RAN) as a pathway to 5G coverage. U.S. policymakers are enthusiastic about O-RAN as an alternative to traditional network models, where Chinese multinational Huawei has emerged as a leading global player. And as growing U.S. private sector interest in India as a manufacturing location illustrates, the potential to build a supply chain ecosystem with India as a hub is increasingly plausible. Following the recent India-U.S. Commercial Dialogue, the two countries signed a memorandum of understanding to set up a semiconductor supply chain and innovation partnership, which aims to promote supply chain resilience and diversification.
A strategic technology partnership between India and the United States should also prioritize developing the standards and principles that govern the technologies of the future. Defining such standards is critical in lowering the costs and barriers for Indian and U.S. tech companies to counter competitors operating from authoritarian states. The two countries will need to work with standards-setting bodies to define how they want emerging technologies to operate in the interests of democracies. Here, the iCET is already taking important steps on academic and industry collaboration. A strategic partnership could build on these efforts and coordinate further resources toward new private sector collaborations.
The two countries will need to work with standards-setting bodies to define how they want emerging technologies to operate in the interests of democracies.
India and the United States must also work together to mitigate the challenges of emerging technologies. Technology cannot be divorced from its implications for human rights, national security, and information ecosystems necessary for functional democracy. This will be vital in 2024, when both India and the United States hold elections. Standards must hold actors to democratic norms (and constitutional laws). As the reach of digital authoritarianism grows, it is more important that networks are hosted by reliable telecommunications vendors that provide secure services and are headquartered in states that operate under the rule of law, such as those preferred by the U.S. and Indian governments.
Finally, the two countries should form a strategic partnership that aims to engage with the global south on how technology can promote shared security, prosperity, and resilience. India has worked to function as a bridge to the wider global south, including in digital infrastructure. A joint approach that unites a competitive package of technologies with a shared U.S.-Indian vision for open societies could serve to extend a hand to nontraditional partners during a key geopolitical moment.
A U.S.-India strategic technology partnership can set a positive trajectory for a tech-driven century. As technology developments transform national security, economic prosperity, and social relations, a transformational partnership between New Delhi and Washington will ensure that these advances arc toward the values of democratic societies.
Think20 India: Bridging the Ingenuity Gap
India assumed its G20 Presidency in the midst of global flux. Post-pandemic recovery efforts were uncertain and uneven; the Ukraine crisis had resulted in supply-chain bottlenecks and consequent global stagflation; and the perennial onslaught of the “elephant in the room”— global warming and climate change—had only exacerbated the challenges.
While unveiling the logo and the theme, PM Modi posited the country as an architect for a forwardlooking and result-oriented agenda for the world and the G20 as an exemplar of change, a vision for sustainability and growth, and a platform engaging with all that matters to the global south. Prime Minister’s vision, of drawing on India’s age-old ethic of Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam, strongly reiterated that inclusiveness and global cooperation would undergird India’s G20 Presidency.
A framework of 4Ds delineates India’s identification of its priorities as President—the promotion of decarbonisation, digitalisation, equitable development, and the deescalation of conflict. This approach is reflected across the thematic areas of Think20 (T20) India—the G20’s official Engagement Group for think tanks—which is often referred to as the “ideas bank” of the G20. The exchange of perspectives among high-level experts, research institutions, and academics that the T20 facilitates lends analytical depth and rigor to the G20’s deliberations. The T20, thus, institutionalised what Thomas Homer-Dixon calls “ingenuity” or the “production of ideas”, and helps bridge “the ingenuity gap”, i.e. the critical gap between the demand for actionable, innovative ideas to solve complex challenges and the actual production of those ideas.
The 4Ds are closely oriented towards the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). As such, these framing ideas or principles are reflected across the T20’s seven Task Forces, which deal with ‘Macroeconomics, Trade, and Livelihoods’; ‘Our Common Digital Future’; ‘LiFE, Resilience, and Values for Well-being’; ‘Clean Energy and Green Transitions’; ‘Reassessing the Global Financial Order’; ‘Accelerating SDGs’; and ‘Reformed Multilateralism’.
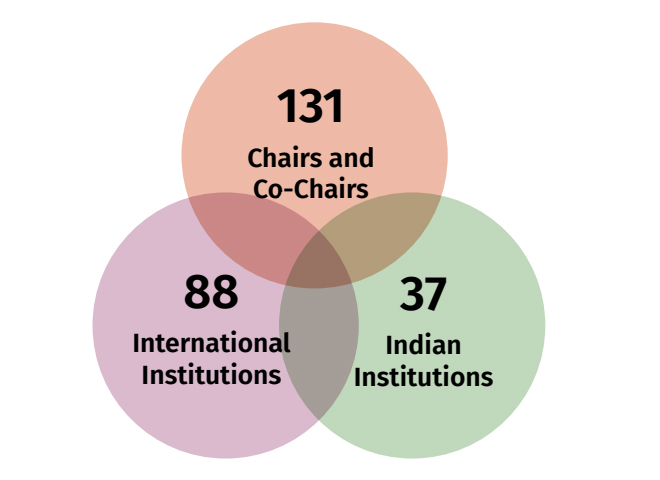
Constitution of Think20 Task Forces
The T20 Mid-Year Conference took place in Mumbai on 10-12 May 2023. Three hundred attendees and Task Force members from across the G20 countries deliberated on the seven selected themes and took stock of the T20’s achievements thus far and the road ahead. Two particular elements of T20 India’s research and engagements stand out—its focus on mainstreaming gender and promoting gender equality, and its efforts to ensure that the African continent is an integral part of all conversations. India, being the second of four successive emerging economies to lead the G20 (Indonesia, India, Brazil, and South Africa will have been G20 Presidents between 2022 and 2025), has not only been a prominent voice of the Global South but has specifically put forth the unique developmental imperatives of the African landmass.
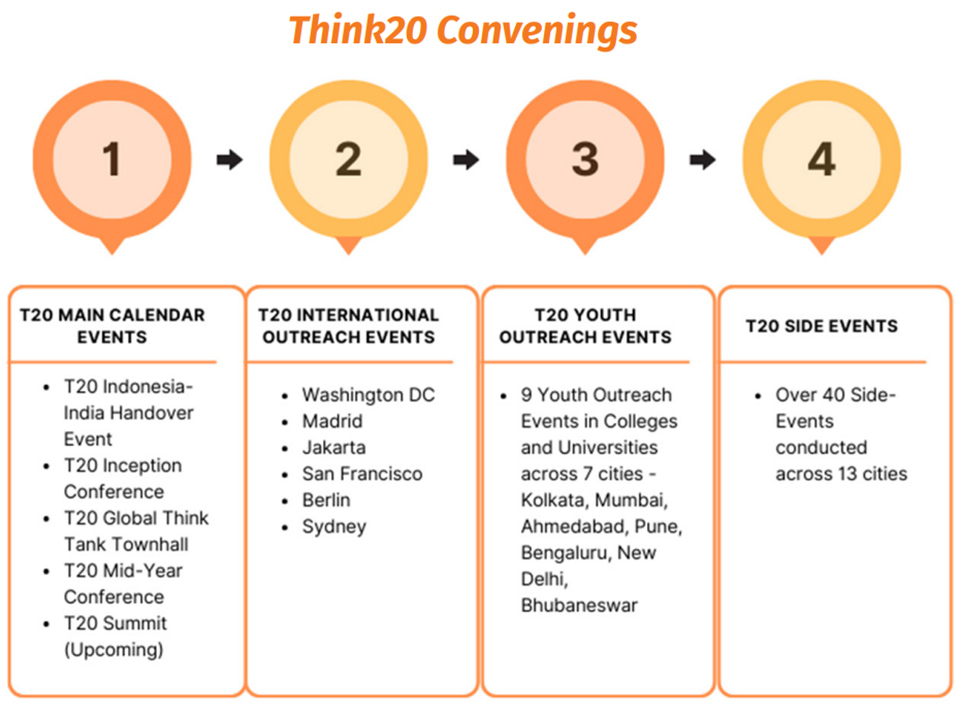
A key activity at the Mid-Year Conference was to finalise the Task Force Statements, which are vision documents about the Task Forces’ areas of engagement. The T20 Communiqué, a summary of recommendations to feed into the G20 process, is being drafted based on these statements and will be launched at the Think20 India Summit in Mysuru in August 2023. Moreover, as the term of the Indian T20 crosses its mid-point, it has already hosted over 50 events across the country and beyond and published over 125 Policy Briefs (PBs) with many more in the pipeline. These briefs are the outcome of processing raw ideas and producing them as actionable inputs.
The ethos of ‘Jan Bhagidari’ (or broad-based civic participation in governance) has underpinned the Indian Presidency’s efforts to take the G20 and its ideas to constituencies such as the youth, women, businesses, and civil society. Recognising the youth and women as essential partners in development and growth, the Mumbai Conference engaged actively with these target groups, and over 100 students from schools, colleges, and universities across Mumbai and Pune took part in the event.
The ethos of ‘Jan Bhagidari’ (or broad-based civic participation in governance) has underpinned the Indian Presidency’s efforts to take the G20 and its ideas to constituencies such as the youth, women, businesses, and civil society. Recognising the youth and women as essential partners in development and growth, the Mumbai Conference engaged actively with these target groups, and over 100 students from schools, colleges, and universities across Mumbai and Pune took part in the event.
The United Nations Security Council is constituted to further the colonisation project
We can all agree today that this has been a very long decade; and it’s only just begun. The fabric of internationalism has been ripped in the last three years, and the ability to forge consensus on many vital questions that can enrich peace and strengthen security is at its lowest in nearly a century. There is a clear need to reform and reshape key institutions of global governance. Certainly, the United Nations Security Council (UNSC), in particular, needs an urgent overhaul.
Yet, we are all aware that the United Nations (UN) process as well the UNSC reform process are going nowhere. It is a fact that only once in the nearly eight decades of the UN’s existence has there been some semblance of reform—when the non-permanent seats of the UNSC were increased from six to 10. Since then, all efforts have largely been exercised in hollow statement-making. Tragically, these statements come with no timelines and are, of course, devoid of any content. Perhaps, this is the right time for this debate. Hence, the idea of bringing in new voices and opening this issue up for debate and discussion to the larger public—to the research community and to academia—must be lauded. We hope that the curious mix of practitioners and thinkers from the Global South can produce some breakthrough solutions that can take this debate forward.
The fabric of internationalism has been ripped in the last three years, and the ability to forge consensus on many vital questions that can enrich peace and strengthen security is at its lowest in nearly a century.
Decades of inaction have also resulted in the prevention of reforms becoming an ideal and an objective in itself. We have seen obstructive tactics, the emergence of a number of clubs and groups on this topic, and a myriad ways of stalling, delaying, and preventing progress. This, now, has become an end goal, and, perhaps, even a key responsibility area for diplomats posted to the hallowed institution that is the UN. That must change. We need to talk about progress in real terms. What should be the new format for engagement? There can be many answers to this question. What diplomats like Ambassador Ruchira Kamboj and academics like Matais Spektor say may not be the only solution. The solution may, in fact, lie in very different viewpoints and voices, and it is imperative that we hear them. Most importantly, we must all agree that status quo is not an answer.
The UN is facing a crisis of credibility as a global institution; and the lack of progress in the reform of the UNSC is going to create complete disenchantment. The future of the UN and its role is intimately linked to the progress made on this subject. Therefore, we must recalibrate our efforts as a global community and make sure that discussions on the reforms are infused with fresh voices and perspectives from geographies that are likely to contribute significantly to a stable and prosperous future. These are also the same nations that are likely to be most affected by a dysfunctional international institution.
Perspectives from the G20 and BRICS
Two recent debates we in India have been engaged in are of relevance to the conversation on institutional reform. One, of course, is courtesy the G20 presidency and its engagement groups that are working on various aspects of multilateral cooperation. Multilateral reforms is one of the most important debates happening in these groups. We are all apprised of the fact that the UNSC, the UN itself, the multilateral development banks, and the financial institutions need a complete overhaul. These institutions are no longer serving us in this particular century. The second is the aspirations of the BRICS. Under South Africa’s Presidency, there is an eagerness for and anticipation of institutions accommodating the aspirations of the African continent—a continent that is rising dramatically and rapidly.
The war is history, and so are the influence and capabilities of some of the members of this erstwhile group of victors.
We can see that different groupings are also beginning to understand and agitate this very important issue. Why is this important? Why mention the G20 and BRICS? The answer is: because we live in a deeply heterogeneous world. Some people also call it a multipolar world. It is untenable that a group of victors of a war from another century should be in charge of managing the world of today. The war is history, and so are the influence and capabilities of some of the members of this erstwhile group of victors. It is time to strengthen the A-Team and bring in voices who can serve all of us better. But beyond this particular aspect, there are three reasons for why we should be thinking about reform.
Why UNSC reform in particular
First, the current structure of the UNSC is perverse and immoral. For many in the Global South, it is a perpetuation of the colonisation project. The burden of the two World Wars was borne by the colonies, while the privileges of peace benefited the colonisers and their allies. Today, that is something that is being questioned by many; and it is increasingly going to become an important aspect of future debates as the world gets impatient with lack of progress in institutional reform.
Second, the reform is important because, currently, the UNSC is inefficient and does not serve the purpose it was installed for. In the past decades, we have seen how the will of the comity of nations has been negated by one or more of the permanent members. More recently, the crisis in Ukraine presents a classic example of the Security Council’s failure to deliver, and it is a stark reminder of why status quo is untenable. The voting patterns and the abstentions on the Ukraine conflict clearly point to the need to bring in others who can contribute to the global efforts around peace and stability.
We are struggling to reform the UNSC due to the nature of the inter-governmental negotiation (IGN) process itself.
Finally, the UNSC is undemocratic and non-representative. How can we accept a structure that shuts out Africa, Latin America, and democratic Asia, including the world’s largest democracy? The Permanent Five (P5) was configured to disproportionately include three European nations. Even having three nations in the P5 could not keep peace in the Old Continent. Clearly, here, three is a crowd. We need to reconfigure how we have structured the P5.
But this may not be the only viewpoint that is valid. There are others as well, and we must respond to and engage with them. For example, Uniting for Consensus argues that there cannot be any permanent membership of the UNSC for new members. This is a viewpoint against permanency and it must be put on the table. But, we must ask, if there is no permanency, why is it not applicable to the P5 as well? Why is it that all UN member states who want to be sitting as credible actors in the UNSC should not gain favour of 129 votes and assume a permanent role? These debates must not be cast aside or shut off. In fact, different groups and different viewpoints must be brought into the same room. And we hope that through this academic track, we can actually bring these varied perspectives together and come up with a mosaic of ideas and, thereafter, a symphony of solution.
To conclude, two points must be highlighted. First, we are struggling to reform the UNSC due to the nature of the inter-governmental negotiation (IGN) process itself. The fact that the IGN process, unlike any other in the UN, needs consensus for both process and outcomes makes it a nonstarter. In no UN negotiation is consensus a precondition for commencement. This is a fatal flaw in the way the process has been stitched together and no progress is possible unless we revisit this core element. Second, what is imperative is a concrete timeline as well. The 2024 Summit of the Future is being touted as a platform where productive discussions about UNSC reforms may finally take place. But the 2024 Summit cannot be regarded as a cure all and a one-stop-shop for everything. We must agree to a two-year timeframe, or a timeframe that others may suggest to be more viable, and we must rigorously adhere to it.
By the time the UN turns 80 in 2025, UNSC reforms must be well underway. Let us make this target a common agenda for all of us, with all our different viewpoints. Let us unite our energies to transform the UN into a multilateral institution that truly recognises the sovereign equality of all member states, and undertakes an operating systems upgrade that will bring it—with the rest of us—into the third decade of 21st century.
This article formed part of the Framing Remarks given by Samir Saran, President, ORF at the Roundtable on, “Shifting the Balance: Perspectives on the United Nations and UN Security Council Reforms from Global South Think Tanks”.
The roundtable also saw the participation of Ruchira Kamboj, Permanent Representative of India to the United Nations; Matias Spektor, Professor of International Relations, FGV, Brazil and Visiting Scholar, Princeton University; and Gustavo de Carvalho, Senior Researcher, South Africa Institute of International Affairs, South Africa.
The new world – shaped by self-interest
A series of far-reaching events are shaping the 21st century. The current conflict in Ukraine, while grabbing headlines and engrossing the G7 summit in Hiroshima, may not seem as pivotal if one is situated in a different part of the world. To most, this is still a festering neighbourhood conflict that Europe must manage. It does not animate lives everywhere; neither does it shape anxieties or future partnerships.
India, Africa and Latin America are not indifferent to the crisis in Europe. They simply have more pressing matters to attend to — the imperatives of nation building being the most urgent. That they now also must navigate the collateral impact of the war makes them all but an interested party.
The first lesson from global reactions to the war is geography still matters. East-West and North-South binaries may be captivating, but proximity and the neighbourhood are considerably more important. We may be hyper-globalised, but we are also more local than ever before. Social media, trends in technology and politics, and a host of other factors have bracketed us into narrow spheres of interest. Thus, while India respects Europe’s difficulties, for it the 2020s began not with Ukraine but with Chinese aggression, the virus from Wuhan and the surrender of Kabul.
Social media, trends in technology and politics, and a host of other factors have bracketed us into narrow spheres of interest.
The second lesson pertains to the UN vote condemning the Ukraine war. Of the 140 countries that voted and condemned Russia, only a fraction sanctioned Russia. Studying the list of countries that were the earliest to receive vaccines in the pandemic could prove to be productive. It might explain which countries have sanctioned Russia. It will also offer valuable lessons about globalisation, its hierarchy and therefore, its discontents. Those sanctioning Russia today are not merely the victors of World War II, but also of globalisation and development. Others are well within their rights to challenge the status quo.
It is often stated, unthinkingly, that India is on the fence. India is not on the fence — it is only standing its ground. It will choose its priorities just as every other country has done. The recent spate of visits by European leaders to China shows that value-based frameworks are untenable. Nations are driven by self-interest and in this case, the need to maintain lucrative economic relations. India is no different. Even as it confronts the Chinese on the Himalayan heights, trade continues where the economy needs it. Distance matters; interest matters even more.
The third lesson derives cumulatively from four recent events: The pandemic; the fallout of the Doha Agreement and the abandoning of Afghanistan; the Chinese aggression on India’s borders; and new sanction regimes and their impact on the loosely termed “Global South”. The Covid-19 outbreak saw the overt hijack of medical equipment and access to vaccines, and growing gaps in treatment capabilities.
Nations are driven by self-interest and in this case, the need to maintain lucrative economic relations.
Indeed, when the pandemic struck, there was no superpower, there was no great power, and there was no big power. There were only selfish powers. Similarly, the Afghan people were betrayed and abandoned because it was expedient for higher powers to flee the country at a particular moment. And Chinese territorial incursions have provoked a range of self-serving responses from different actors otherwise keen to defend democracy.
Put bluntly, there is no moral high ground. All that remains is the ruthless pursuit of national self-interest. Two actors epitomised this approach in the 1960s and 1970s, one actor in the 1980s and 1990s, and several new voices have joined the fray in this century.
If meaningful international dialogue is to be conducted, nations must right-size some of their perceptions about each other and themselves. In this context, the tendency to frame the Global South as a possible bridge actor between competing positions has its merits. But the “Global South” is itself a deeply reductive term, which elides the group’s innate heterogeneity. Very few countries would like to be categorised as “southern” as they continue to rise and shape global systems. Five years from now, Brazil and India might bristle at such a label themselves.
The neatly packaged idea of the Global South fails to recognise that there will soon be far more decisive swings within the group than outside it. How the countries of the South organise themselves over the next decade will have a far more profound impact than the West on the global balance of power, and on the contours of the new world order. As this century progresses, an East and West will emerge within the Global North and South.
LLPs will come to constitute the geometry of politics, and countries will work together on specific issues, for specific purposes, and for specific outcomes.
Concomitantly, international engagements of the future will organise themselves around the standard operating principle of law firms — as limited liability partnerships (LLPs). LLPs will come to constitute the geometry of politics, and countries will work together on specific issues, for specific purposes, and for specific outcomes. With the transition to the new LLP ethos of geopolitics, we will not be burdened by the need to focus on anything other than the narrowly defined collaborative interest at hand, and can build relationships that are more strategic, if also more transactional. This is a gritty, realist world. We may not like it, but it’s here — and here to stay.
The just transition framework is unjust
The idea of a “just transition” away from fossil fuels is now a common refrain in the climate debate. However, what constitutes such a transition remains narrow, ambiguous and difficult to apply in most contexts. The current framework, originating from the Global North, emphasises the “just” need to provide alternative “green jobs” to coal workers at risk from the desired energy transition; in other words, it seeks to replace coal power plants with green energy sources and minimise its societal collateral. In contrast, the developing world may want to focus on a more comprehensive economy-wide transformation, linking just transitions to broader issues of energy security, poverty reduction, and climate finance.
Despite this gap in ambitions and aspirations, the G7 has recently been pushing a new international mechanism for implementing just transitions in emerging economies — Just Energy Transition Partnerships (JET-P). These arrangements demand ambitious coal phase-out targets from recipient countries in exchange for G7 financial support. The “just” component includes social considerations during the transition. Already South Africa ($8.5 billion), Indonesia ($20 billion), and Vietnam ($15.5 billion) have signed onto JET-Ps.
India has repeatedly declined to engage on this issue due to a substantial disconnect between the G7 and its idea of what constitutes a “just transition”. India has strongly opposed the demand to include specific targets for phasing out coal, reiterating that any deal which requires a potential tradeoff between development and decarbonisation cannot be considered “just”, as growth and development gains in the G7 countries have been and still continue to rely on fossil fuels.
The coal sector in India employs an estimated 3.6 million people (direct and indirect), compared to around 100,000 workers in South Africa.
The nature of India’s coal economy does not lend itself to the existing structure of JET-P deals. The coal sector in India employs an estimated 3.6 million people (direct and indirect), compared to around 100,000 workers in South Africa. The impact of an unplanned transition would be substantially larger in India. Moreover, JET-P benefits are unlikely to reach the more vulnerable informal, low-income, and non-unionised workers in the sector.
Finally, the current JET-P relies heavily on loans, which are not well suited to address the social aspects of the transition. Providing alternative livelihoods for coal workers will necessitate an economic transformation of coal-dependent districts and re-skilling of coal workers, which will require grant-based and concessional financing.
The G7 countries will continue to struggle to reach a deal with India unless they can reimagine what constitutes “just” and what may be an optimal “transition”. To resolve this, there is a need to preserve the ethic of animating JET-Ps while being open to operationalising these in discreet ways for specific geographies. The focus, therefore, must be on deploying funds to enable transformative change that complements existing decarbonisation efforts, creates the maximum bang for the buck, and crowds in a flow of capital larger than the footprint of the scheme. And most importantly, rather than obsessing with coal, CO2 reduction must become the principal outcome.
For example, deploying even about $20 billion for a deal to phase out a few coal plants in India would only result in a small mitigation impact, and this, too, may fade in relative terms as funding dries up. The budgeted outlays could instead be deployed in other ways for more compelling outcomes.
India is showcasing great ambition in decarbonising several sectors of the economy. A similar amount deployed in these sectors can have a transformative impact by crowding in additional capital that aligns with India’s development agenda. This would also help position India as a solution provider for these sectors for other developing and emerging economies. Two areas, in particular, hold much promise for such a reconceptualised JET-P.
A JET-P for this sector could have a catalytic effect by directing funding towards augmenting R&D and developing a manufacturing base for climate-friendly technologies.
The cooling sector is one of these. Cooling demand in India is expected to increase eight-fold by 2038 as affordable thermal comfort will be closely linked to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals. The World Bank estimates that a green cooling pathway could unlock a $1.6 trillion investment opportunity by 2040 with the potential to create a massive 3.7 million jobs. A JET-P for this sector could have a catalytic effect by directing funding towards augmenting R&D and developing a manufacturing base for climate-friendly technologies. India’s Cooling Action Plan would be boosted further by such financial flows.
Electric mobility is the second big opportunity. In 2022, India hit a million electric vehicle sales for the first time and is expected to become a $100-billion industry by 2030. India already has multiple policies in place to create a complete EV ecosystem, covering vehicle manufacturing, batteries, and charging infrastructure. A JET-P could look to aid these efforts and channel investments to nascent EV segments, such as long-distance freight and passenger transport. JET-Ps could also explore options to utilise grant-based funding for the reskilling of millions of workers currently employed in the ICE ecosystem.
In sum, the G7 should adopt a smart and country-specific approach. Instead of using JET-Ps to further its own agenda, it must look to prioritise the delivery of transformative agreements that align with the recipient countries’ objectives for significant and lasting impact.
Why India is key to 21st century multilateralism
Four watershed events since 2020 — a short period, but with apologies to Lenin, decades have happened in this time — have established India’s credentials as one of the last major bulwarks of a rules-based order, open and fair trade and economic arrangements, and the rule of law. These are critical elements if we are to build a new world order that is balanced, inclusive and fair.
The first event was the capitulation of western powers in Afghanistan. The triumph of the Taliban was not a victory by just war but the defeat of a people by deceit. Liberals around the world were kept in the dark as a Faustian bargain was struck by major powers that sought expediency over ethical diplomacy. Today, American supporters of the infamous Doha Agreement — ironically called the Agreement for Bringing Peace to Afghanistan — express concern about Afghan women. Their hypocrisy is naked and jarring. The Doha deal could never have turned out any differently. India kept a principled distance from that pernicious deal. Appreciating fully the true nature of a prospective Taliban regime, it continued to seek an elected and pluralist government in Kabul. India was a lone voice. Yet it did not compromise. Today, India continues to support the people of Afghanistan without recognising the regime that tyrannises it.
American supporters of the infamous Doha Agreement — ironically called the Agreement for Bringing Peace to Afghanistan — express concern about Afghan women.
The second is the war in Ukraine. The measures and countermeasures by Russia and Ukraine have resulted in bloodshed and mayhem, ultimately perpetuating the conflict. India’s position of principled independence, while advocating cessation of violence and pursuit of diplomacy, is recognised as the only meaningful way forward. The Indian stance has resonated across the G20 and beyond. The G20 Bali Leaders’ Declaration echoes Prime Minister (PM) Narendra Modi’s approach when it speaks of the “need to uphold ….. the multilateral system that safeguards peace and stability”, the importance of “peaceful resolutions of conflicts”, and the vital role of “diplomacy and dialogue”. Furthermore, India has consistently argued for respect for sovereignty and investigation of crimes against humanity, including those possibly committed by the Russian army.
Third, in the technology domain, India has long championed an open, free and fair digital order. However, with the United States (US) pressing for narrow benefits for Silicon Valley in the past decade, India was reluctant to endorse instruments that sought free data flow without sufficient accountability from actors responsible for storing and transporting such data. Much to the US’s chagrin, India appeared to restrict cross-border data flows, sought regulation of non-personal data and contested monopolies, and restricted cartelisation attempts of the US’s payments and e-commerce companies. It made no secret of its distrust. Having dispelled coercive pressure to enter into digital handshakes on unfavourable terms or sovereign commitments on a future digital services tax, India has now eased its stand on data localisation. The reason: There is no longer any pressure from the US because even domestic actors in America want greater regulation and accountability from Big Tech. India is exploring sharing data with “trusted geographies” while seeking surgical data protection for specific sectors. An inclusive, equitable internet remains a core priority.
With the United States (US) pressing for narrow benefits for Silicon Valley in the past decade, India was reluctant to endorse instruments that sought free data flow without sufficient accountability from actors responsible for storing and transporting such data.
The year 2021 signalled India’s fourth landmark moment. At the 26th round of the Conference of the Parties (COP26), India demonstrated extraordinary commitment to the planet by announcing its goal of reaching net-zero by 2070. It voluntarily imposed on itself a timeline for climate action, although its emissions per capita were well under two tonnes – about one-eighth those of the US. PM Modi’s Panchamrita road map for 2070 includes interim targets for boosting non-fossil energy capacity, using renewables, and reducing carbon emissions and the economy’s carbon intensity. PM Modi also later launched India’s LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) Mission. He emerged as one the earliest world leaders to state candidly that climate action would require changes to individual lifestyles, taking steps to initiate those changes. By contrast, an international survey of 10 countries, including the US, the United Kingdom, France and Germany — published to coincide with COP26 — found few citizens willing to make significant lifestyle sacrifices. In fact, 46% of respondents believed there was no real need for them to do so. Take the facile but heated domestic debate around a potential ban on gas stoves in the US. Even as US diplomats have long championed “clean cookstoves” for the developing world, it appears there is little interest in following good climate practices at home.
India’s natural influence as a democracy and sincere interlocutor that can engage the political spectrum of nations gives it unique moral authority. Indeed, 21st century multilateralism needs more Indias. The G20 — with its mix of developing and developed countries — offers the perfect platform for India to infuse partner nations with foundational ideas. The world has much to learn on putting humanity first, adopting a pro-planet orientation, promoting peace, and placing equity and inclusion at the heart of internationalism. With its ethos of One Earth, One Family, One Future, India could show the way.
India will prioritise data for development at G20
At the G20 Leaders’ Summit in Bali last month, Prime Minister (PM) Narendra Modi pledged that the principle of “data for development” will be integral to India’s G20 presidency. New Delhi’s commitment to this principle and its vision of strengthening it through international cooperation are already apparent. The first side event of the G20 Development Working Group under the Indian presidency, held in Mumbai on Tuesday, addressed the theme “Data for development: The role of the G20 in advancing the 2030 Agenda”. Amitabh Kant, India’s G20 Sherpa, emphasised that the country’s strategic use of data for governance and public service delivery in its aspirational districts, for instance, has, in three years, wrought a transformation that would otherwise have taken six decades. Data has also powered India’s pandemic response, innovations in education, health care, and food security, and enabled digital financial inclusion at a near-population scale.
As a group composed of developed and developing nations, the G20 presents a microcosm of what a concerted global effort to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) might resemble. If the G20is to help accelerate progress towards SDGs, it must vigorously pursue two kinds of data-driven interventions: Rejuvenating legacy datasets using Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Big Data analytics, thus converting data to intelligence; and using cutting-edge emerging tech — including drones, geospatial mapping, and AI — to generate futuristic new datasets.
The country is about to launch a major data initiative as a part of which it will share anonymised data sets collected under the National Data Governance Framework with the AI ecosystem, and the research and startup communities.
In both areas, India has much to offer the world. The country is about to launch a major data initiative as a part of which it will share anonymised data sets collected under the National Data Governance Framework with the AI ecosystem, and the research and startup communities. This vast database will be used to train AI models, catalyse innovation, and craft more effective policy and on-ground solutions. In May, NITI Aayog launched the groundbreaking National Data and Analytics Platform to democratise access to public government data by making datasets accessible and interoperable, and providing accompanying tools for analytics and visualisation. Each of these initiatives builds upon the PM’s vision of a Digital India characterised by a digitally empowered society and tech-enabled knowledge economy.
The creation of entirely new datasets is also exploding in India. Drones are scanning the country’s terrain in minute detail, and this aerial footage is being combined with other kinds of data to create extraordinarily detailed maps. Data generated by drones is also revolutionising agriculture and helping transform existing cities into smart cities. The World Economic Forum estimates that the new data economy resulting from drones could boost India’s Gross Domestic Product by $100 billion and create nearly half a million jobs in the coming years.
Indeed, India is rapidly emerging as a world leader in the geospatial sector. Addressing the United Nations World Geospatial Information Congress in Hyderabad in October, PM Modi emphasised that geospatial technology is a “tool for inclusion” that has been “driving progress” and established itself as an enabler across development sectors. In fact, this is a space in which India has already begun to support its South Asian neighbours with communications and connectivity.
Across nations, data must be emancipated from its current silos, and progressively larger volumes of data must be made public and easily discoverable.
As India and its G20 partners forge collaborations centred on data for development, they should adhere to certain core principles. Across nations, data must be emancipated from its current silos, and progressively larger volumes of data must be made public and easily discoverable. To be used effectively, data must be simple, high-quality, and offered in real-time. A culture of experimentation and innovation must be fostered around data operations, and countries must invest in tools for analysing datasets in creative ways. To enhance outcomes, constructive competition could be promoted among stakeholders in the data ecosystem.
Two crucial tasks lie before the G20. Its members will have to try and arrive at a common understanding of sensitive and non-sensitive data, and to reflect on frameworks that could help share data across borders. There is an in-principle consensus that open repositories should be built where nations can store public-value data. But a prudent balance will need to be struck between the imperatives of data sovereignty and protection, and the notion of a data commons that could benefit the global community. Ultimately, the G20’s data regulations should embed the norm of reciprocity — nations should be able to share and benefit from development data.
A culture of experimentation and innovation must be fostered around data operations, and countries must invest in tools for analysing datasets in creative ways.
As 2030 nears, the Indian presidency could be an inflection point for the G20’s deliberations around data for development. Since 2019, the theme’s importance has been consistently reaffirmed by G20 leaders, and the recent Japanese, Saudi Arabian, Italian and Indonesian presidencies have all recognised that the wealth of data produced by digitalisation must be harnessed. But government-to-government dialogue must increasingly be supplemented by systematic engagements with the private sector, civil society, women and young people, if data-led empowerment is to be mainstreamed. This is a key element India could underscore in the G20 playbook, thus shaping past achievements and present priorities into what could become a part of the grouping’s legacy to the world.